Spreadsheet Model Risk Management (MRM) and Compliance
End User Computing Artifact (EUCA) Risk Management
End user tools such as spreadsheets have empowered ordinary users to
build
simple applications without relying upon centralized information
technology
departments. That in turn has freed resources in those
departments to support
large scale enterprise applications which require a
professional level of expertise.However, these EUCAs are generally not developed with the same review mechanisms used by IT professionals. There have been many studies which show that spreadsheets and other EUCAs often contain serious errors. EUCAs may be relatively simple, but that does not mean that they are not important. Critical business decisions are often based upon EUCAs, and millions of dollars have been lost due to spreadsheet errors. It has been well said that if a transaction involves thousands of dollars it is probably processed by a professionally managed database, but if it concerns millions of dollars then it is probably analyzed by a spreadsheet.
Excel Model Risk Management
Organizations should have a risk management strategy that minimizes the risk of EUCAs while still enjoying the benefit of small scale ad hoc development. Such a strategy should entail the following steps:-- Identify the EUCAs, their location, who is using them, and for what purpose.
- Determine the risk profile of each EUCA. This can be
based upon
- How critical the models are, and what the cost of a potential error might be.
- How complex the models are, and how likely they are to contain substantial errors.
- Mitigate the risk with a focus on EUCAs that are both complex and critical. This can involve peer reviews, independent modeling, or possibly re-implementing the model using a different technology.
The Spreadsheet Detective
The Spreadsheet Detective is a well established tool for minimizing errors in individual models. It also provides tools that facilitate peer review of important spreadsheets. Details can be found here.The Compliance Detective
 The
Compliance Detective provides tools that can be used to implement a
risk management strategy. Specifically it can
The
Compliance Detective provides tools that can be used to implement a
risk management strategy. Specifically it can- Generate metadata that describes the potential risk that a
spreadsheet creates. This can be
- Automatically derived, such as calculating the number of
distinct (unique)
formulas within a model,
- Manual entered, such as recording the criticality of a model, or
- Calculated from other values, such as calculating the risk
based on complexity
and criticality.
- Collect the metadata so that it can be reviewed by risk
management experts. This can be performed by
- A high speed scanner that can find spreadsheets distributed throughout an organization, or
- A cloud based solution in which metadata is uploaded to
remote servers.
- Analyze the metadata to identify areas of risk that need
attention, as well as to identify changing trends in risk profiles.
- Respond to risks by facilitating remedial strategies and alerting
key stakeholders of potential problems.
Another key factor is to recognize that many spreadsheets are based upon a template that is copied and then modified. Those modifications may only involve data, or they may involve the addition or changing of formulas in the original template. The Spreadsheet Detective can distinguish between formulas that were in the original template and those that were added to the given instance of that template. Once a template has been properly reviewed and certified, it is important to only require a review of added or changed formulas in the instances in order to ensure that the compliance process does not place an unnecessary burden upon spreadsheet users.
The Compliance Detective integrates with existing records management systems. Many organizations already have systems for storage and control of sensitive documents, of which spreadsheets are only one type. The Compliance Detective does not require that spreadsheets be stored in some separate repository, which would then require additional configuration and management.
The Compliance Detective also requires minimal support from an IT department. The Spreadsheet Detective is an ordinary Excel add-in which can be easily installed by end users. It does not require administrator privileges to be installed. The scanner can also be run on any machine that has access to the individual spreadsheets, while the cloud based approach requires no IT support at all as metadata (only) is uploaded directly by individual users.
Metadata Creation
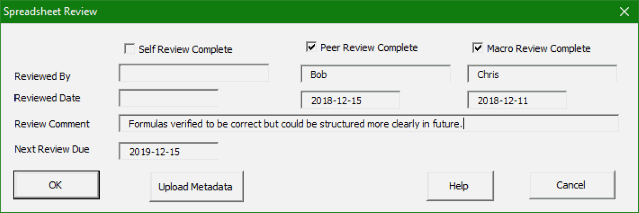
The first stage is to create the metadata that will enable spreadsheets to be managed effectively. Different organizations require different metadata to be collected, so this is highly configurable.Below is an example of a typical form that is expected to be filled out by users for every spreadsheet that is created. It captures basic information about the nature of the model, and most importantly how critical its correctness is to the business.
If the cloud based approach is used then pressing the Upload Metadata button will update the information that is stored in the cloud. This button would not be present in a system that uses the scanning approach.
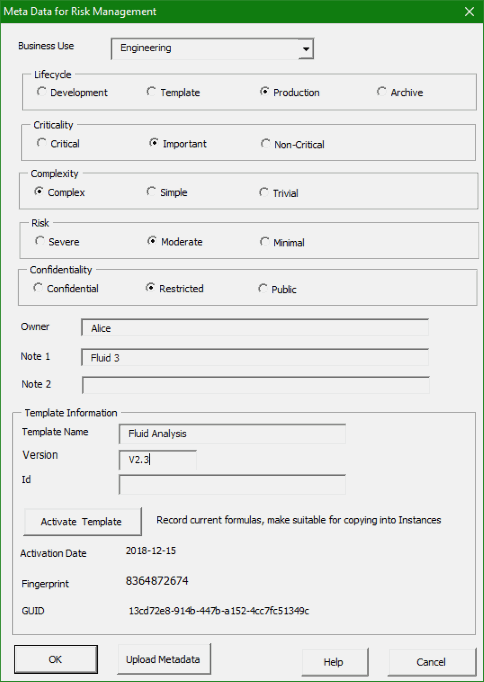
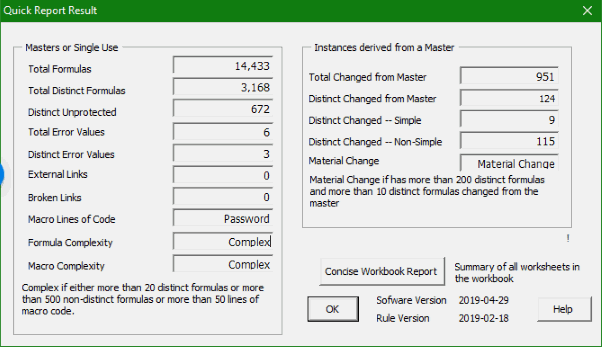
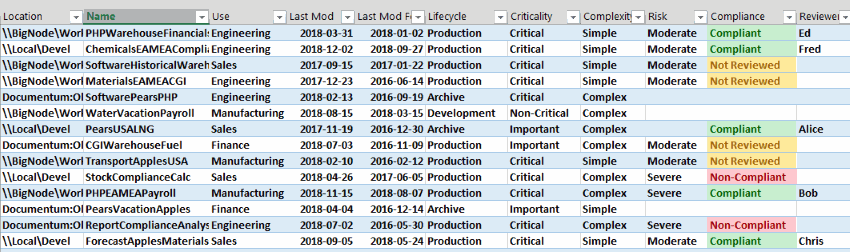
Some information can also be captured automatically. The following shows information about the complexity of a spreadsheet model. Notice that it distinguishes between formulas in a master template and formulas in an instance that is derived from that template.
Review
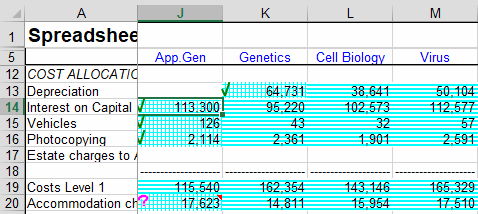
By far the most important technique to minimizing spreadsheet risk is to perform a systematic review of each critical model. This should be performed by someone other than the person that created the model.The Spreadsheet Detective has many powerful tools to assist with such a review. In the image below, the blue shading shows how formulas have been copied throughout a model, and highlights any inconsistencies. The reviewer has then examined just the distinct formulas and marked them as being correct using the green tick, with the exception of the formula in cell J20. These queried cells can then be collected together in a report that can be presented to the original author.
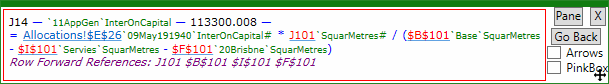
The following dialog clarifies the meaning of the specific formula in cell (J14). Note the green "AutoNames" which indicate which cells the otherwise cryptic A1 references refer to. The purple annotation indicates potential errors or stylistic issues with the model. Clicking on hyperlinks facilitates navigation, and dependents can also be shown. There are videos that describe these and many other features in detail.
When the review is complete the review(s) can update the metadata appropriately. For some models it can be appropriate to also provide a date at which another review should be performed. The Spreadsheet Detective also provides advanced facilities for comparing different versions of a model.
Scanning
The scanning tool can scan many thousands of spreadsheets per hour across an entire organization. It can also directly scan models stored in secure document management systems without needing to download them onto any file server. For larger organizations, incremental scans can be performed that only scan models that have changed since the previous scan. Fingerprinting is used to determine whether formulas have changed rather than just data.Spreadsheet dependencies can be tracked to ensure that upstream data sources are also being used correctly. It can also identify orphaned spreadsheets that continue to be used for some critical business process but are no longer being maintained. Perhaps more importantly, it can help identify applications that are too critical and data centric to be be performed by a spreadsheet at all.
The output can be stored into a database, or can be simply loaded directly into a spreadsheet for analysis.
Cloud
The cloud based approach loads metadata into the Spreadsheet Detective's secure servers. This approach requires no support from a company's IT department. The metadata can also load data into a private cloud if desired.The data can then be analyzed online, or more likely downloaded and analyzed with more powerful offline tools.
Note that only the metadata is uploaded, the actual spreadsheets never leave the corporate network. Any upload requires an explicit user action. And this feature is not available at all unless it has been specifically requested when ordering the Spreadsheet Detective (there is no extra charge).
Analyze
Finally, the metadata can be analyzed to understand the risk profile of an organization. This can be used to target compliance initiatives to where they are most needed.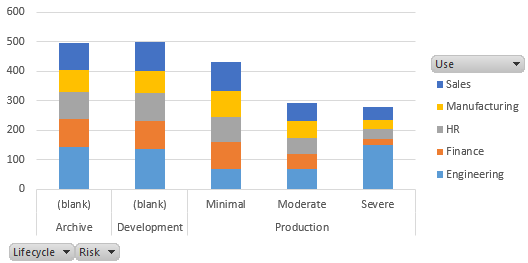
As an example of a typical analysis, we first examine the number of models used in Production as opposed to being under Development or just Archives of old models. We note the risk profile of those models, and for what purpose they have been created.
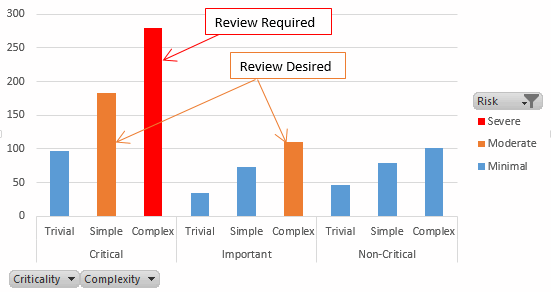
In this scenario, Complex models that are Critical must be reviewed. Those that are Simple and Critical, or Complex but just Important should be reviewed but there is no insistence upon that. Non-Critical models or Trivial ones never need a review.
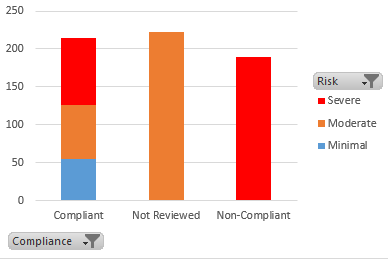
This report shows that our compliance levels are poor. There are almost 200 Complex, Critical models that have not been reviewed, and even more for which a review is desirable but has not been performed.
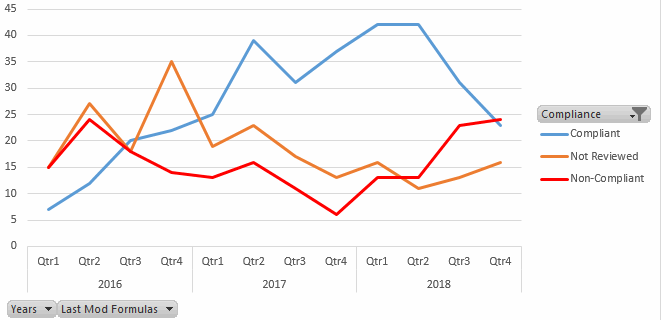
Drilling down, we see that compliance actually improved during 2016 and 2018, with only 6 non-compliant models in Q4 2017. But there has then been a serious regression in 2018.
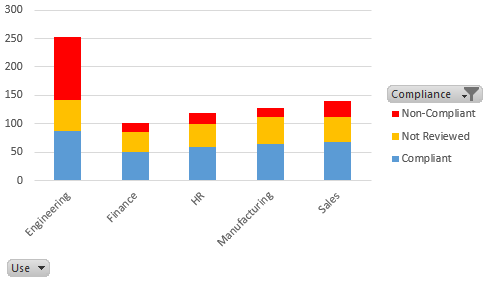
Examining by usage, we see that Engineering has been the major source of non-compliant models.
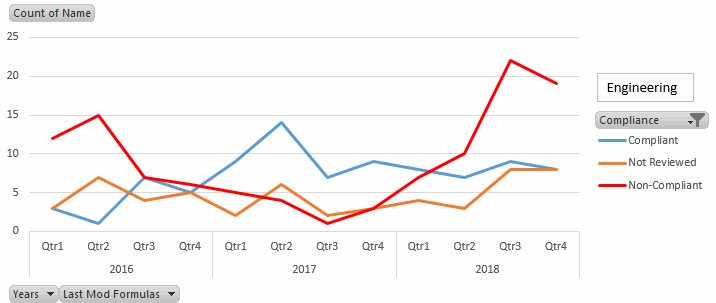
And filtering by Engineering shows that this problem has become much worse in late 2018. Further, the total number of models has increased, which suggest that Engineering has become very busy and may not have time to perform required quality assurance. This could lead to substantial costs if failures should result, so it would appear that Engineering needs additional resources to implement proper risk management.
Conclusion
The Compliance Detective provides tools to gather metadata about spreadsheet models both manually and automatically. This can then be collected either by a scanner or a cloud based approach. The results can be analyzed to develop quality management processes.Perhaps more importantly, the associated Spreadsheet Detective provides powerful tools to perform reviews of complex models, and thus minimize the risk associated with end user computing.